Communicable Disease: Infectious disease that can be transmitted from an infected person, animal, or reservoir to a susceptible host.
- Disease Reservoir: A living (e.g. person, animal, or plant) or nonliving site (e.g. soil or water) where an infectious agent/disease naturally lives and multiples.
- Example: A bat with rabies or Legionnaires in a water-cooling tower.
Contact: A person who has been exposed to an infectious disease.
Direct Transmission: An infectious disease spreading through direct contact. Direct person-to-person contact: an ill person touches or exchanges body fluids with another person (this can be done by an ill person coughing or sneezing near/on someone).
- Example of direct transmission: A person gets the flu from their significant other during a kiss.
- Example of indirect transmission: An ill person coughs into their hand and then touches a doorknob. Later a second person touches the same doorknob, then touches their face, and becomes infected.
Disease Vector: A carrier of disease that transmits the disease to another living organism.
- Examples: Mosquitos are a vector for West Nile Virus and ticks are a vector for Lyme disease.
Exposure: Having a feature that is being studied. Exposures can be medication use, diet, genetics, employment, behaviors, occupation, etc.
- Examples of possible “exposures”: smoking, eating a high fat diet, working outside, playing football, etc.
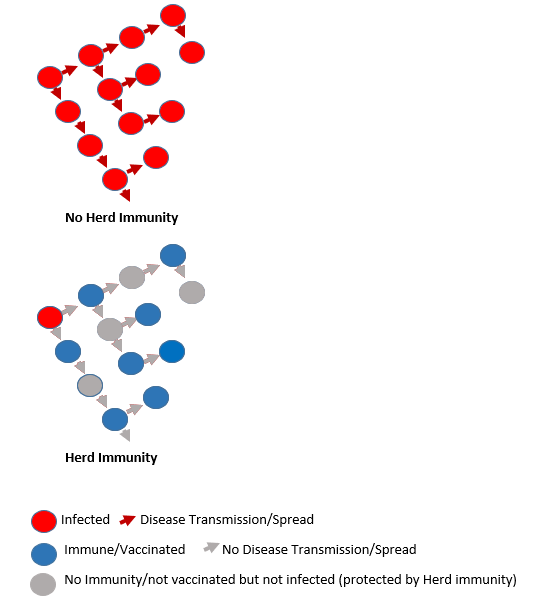
Herd Immunity: Group protection from the spread of an infection based on a high proportion of individuals within a group with resistance. So if a large percentage of the population is immune/resistant to the disease, the entire population is protected. For example, the more people with measles vaccinations in a group, the less ability measles has to spread among the group. Those who are vaccinated stop the disease from spreading, protecting those who have not yet been or cannot be vaccinated.
Host: A person or other animal that harbors an infectious agent.
Incident case: Newly acquired case of a disease or outcome.
Incubation Period: Period of time between exposure and when disease signs and symptoms appear.
Infectious Period: Period of time when the infected can transmit or spread the infection to others.